
Researchers at Trend Micro have discovered bad actors exploiting an Oracle WebLogic Server deserialization vulnerability CVE-2019-2725 to install a Monero cryptocurrency miner.
Oracle patched the remote code execution vulnerability CVE-2019-2725 as part of the April 2019 security advisory. The risk is high given the bug is remotely exploitable without user authentication. In other words, attackers can exploit over the network without a username and password.
Administrators should also take note that the patched vulnerability is rated CVSSv3 base score of 9.8 (10 being the highest possible). So, organizations should make this patch a high priority.
Soon after the April advisory, researchers from SANS ISC wrote about how active exploits were used to install cryptocurrency miners. However, Trend Micro now says attackers are using new tactics.
“The malware hides its malicious codes in certificate files as an obfuscation tactic,” Trend Micro said in the report.
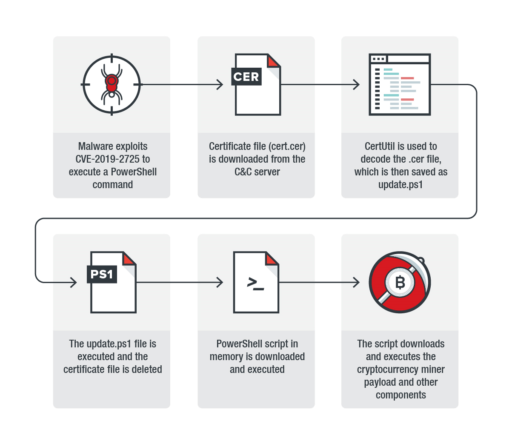
Infection chain steps
Trend Micro released details of the infection chain that consists of six steps as described in Figure 1 below:
- The malware exploits CVE-2019-2725 to execute PowerShell command.
- A certificate file is downloaded from command-and-control server.
- CertUtil (used to manage certificates in Windows) decodes the certificate file. It then saves the files as update.ps1.
- The update.ps1 is executed and the cert file is deleted.
- PowerShell script in memory downloads, then executes.
- The script then downloads and executes the cryptocurrency miner onto target system.
Given Oracle has already patched the bug in April, organizations should upgrade their Weblogic servers to the latest version as soon as possible.
Related Articles
- KryptoCibule malware: triple threat to cryptocurrencies
- Open ADB port attacks spread cryptocurrency-mining botnet
- BabyShark malware expands targets to cryptocurrency industry
- Misconfigured Docker containers abused to deliver cryptocurrency mining malware
- New Rakhni trojan can encrypt files or mine cryptocurrency
