Palo Alto Networks Unit 42 researchers released a new report that highlights how attackers are exploiting remote code execution (RCE), cross-site scripting (XSS), traversal and information disclosure vulnerabilities in multiple vendor products.
Released on August 19, 2022, the new Unit 42 report “Network Security Trends” summarizes key observations from 93 million attack sessions in the wild. The findings are also based on “availability of proofs of concept (PoCs), the severity of the vulnerabilities the exploits are based on and the ease of exploitation.”
Some of the commonly exploited RCEs included vulnerabilities in VMware ONE Access and Identity Manager and Spring Cloud Function, Spring MVC and Spring Web Flux, among other products.
Moreover, the security team also noted threat actors exploiting an XSS vulnerability in WordPress core, as well as SQL injection vulnerabilities in VoIPmonitor GUI and other services.
Commonly exploited CVEs
The Unit 42 report highlighted the following actively exploited vulnerabilities from February to April 2022:
- CVE-2022-22954: VMware Workspace ONE Access and Identity Manager contain a remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability due to server-side template injection.
- CVE-2022-22963: In Spring Cloud Function, when using routing functionality, it is possible for a user to provide a specially crafted SpEL as a routing expression that may result in remote code execution and access to local resources.
- CVE-2022-22965: A Spring MVC or Spring WebFlux application may be vulnerable to RCE via data binding. The specific exploit requires the application to run on Tomcat as a WAR deployment.
- CVE-2022-25060: TP-LINK was discovered to contain a command injection vulnerability via the component oal_startPing.
- CVE-2022-22947: In Spring Cloud Gateway, applications are vulnerable to a code injection attack when the Gateway Actuator endpoint is enabled, exposed and unsecured.
- CVE-2022-24112: An attacker can abuse the batch requests plugin to send requests and bypass the IP restriction of Admin API. A default configuration of Apache APISIX (with default API key) is vulnerable to RCE.
- CVE-2022-22536: SAP NetWeaver Application Server ABAP, SAP NetWeaver Application Server Java, ABAP Platform, SAP Content Server and SAP Web Dispatcher are vulnerable for request smuggling and request concatenation.
- CVE-2021-24762: The Perfect Survey WordPress plugin does not validate and escape the question_id GET parameter before using it in a SQL statement in the get_question AJAX action, allowing unauthenticated users to perform SQL injection.
- CVE-2022-21662: Low-privileged authenticated users in WordPress core are able to execute JavaScript/perform stored cross-site scripting attacks, which can affect high-privileged users.
- CVE-2021-43711, CVE-2022-25075: The downloadFlile.cgi binary file in TOTOLINK has a command injection vulnerability when receiving GET parameters.
- CVE-2022-25134: A command injection vulnerability in the function setUpgradeFW of the TOTOLINK Technology router allows attackers to execute arbitrary commands.
- CVE-2021-4045: TP-Link Tapo C200 IP camera is affected by an unauthenticated RCE vulnerability, which is present in the uhttpd binary running by default as root. The exploitation of this vulnerability allows an attacker to take full control of the camera.
- CVE-2022-24260: A SQL injection vulnerability in VoIPmonitor GUI allows an attacker to escalate privileges to the Administrator level.
- CVE-2021-21881: An OS command injection vulnerability exists in the Web Manager Wireless Network Scanner functionality of Lantronix PremierWave.
- CVE-2022-21371: There is an easily exploitable vulnerability in the Oracle WebLogic Server that allows an unauthenticated attacker with network access via HTTP to compromise Oracle WebLogic Server.
- CVE-2022-27226: A cross-site request forgery (CSRF) issue in /api/crontab on iRZ Mobile Routers allows a threat actor to create a crontab entry in the router administration panel.
- CVE-2022-29464: Certain WSO2 products allow unrestricted file upload with resultant RCE.
- CVE-2021-20167, CVE-2021-20166: Netgear RAX43 command injection vulnerabilities.
- CVE-2021-39226: Grafana Labs Grafana Snapshot authentication bypass vulnerability.
- CVE-2021-28169: Eclipse Jetty information disclosure vulnerability.
- CVE-2021-31589: BeyondTrust remote support cross-site scripting vulnerability.
Unit 42 summarized that RCE is the leading category of attack, followed by traversal attacks, and then information disclosure (see Figure 1):
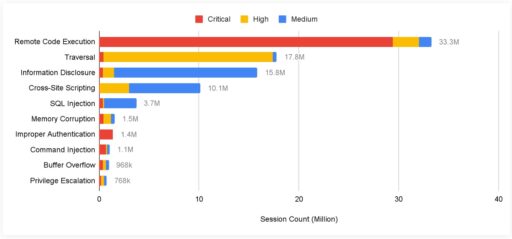
Moreover, the researchers added most of the attacks originated from the United States (74.1%), followed by Germany (4.2%) and Russia (2.8%).
In conclusion, the report summarizes that unpatched web applications remain popular targets for attackers. Bad actors will likely continue to rapidly exploit critical vulnerabilities as POC’s become publicly available.
Readers can check out related articles below for more details on some of the previously mentioned exploited vulnerabilities.
Related Articles
- VMware releases Critical security updates (updated with known exploits for CVE-2022-22954)
- Threat actors exploit Spring4Shell to weaponize and execute Mirai botnet
- Spring fixes Critical Spring Framework “Spring4Shell” and Spring Cloud Function vulnerabilities
- Microsoft January 2022 Security Updates address 10 Critical vulnerabilities
- SAP February 2022 Security Patch Day addresses Critical log4j and ICMAD vulnerabilities
- CISA adds 7 vulnerabilities to Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog (to include Dirty Pipe Linux kernel vulnerability)

