Security experts have discovered a new version of ViperSoftX, a malware that steals cryptocurrency and targets password managers, such as KeePass and 1Password.
According to Trend Micro research, the latest ViperSoftX malware campaign uses different methods than previous campaigns, such as DLL sideloading for its arrival and execution technique. The malware also uses basic anti-C&C analysis by disallowing web browser communications.
“We also noted that this update includes a more sophisticated encryption method of byte remapping and a monthly change in command-and-control (C&C) server,” Trend Micro wrote in a blog post.
“Without the correct byte map, the encrypted shellcode, including all components and relevant data, cannot be correctly decrypted, making decryption and analysis of the shellcode more time-consuming for analysts,” the security firm added.
Moreover, Trend Micro confirmed a “significant number of victims” in the consumer sector were discovered in Australia, Japan and the United States. Enterprise sector organizations in Southeast Asian countries were also affected.
Infection flow
The researchers surmise the bad actors behind the campaign try to trick users into downloading malicious software disguised as bootleg software versions of key generator, an activator, or a patcher.
Trend Micro described the infection workflow in a diagram (see Figure A) and four stages:
- Initial execution
- First-stage loader
- Second-stage loader and main ViperSoftX malware
- ViperSoftX main routine.
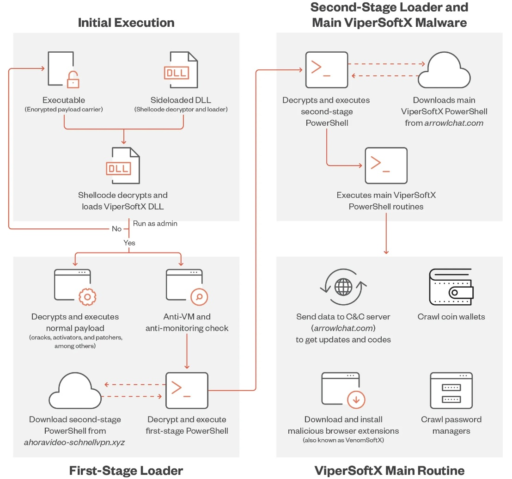
“Actors behind ViperSoftX take this narrative a step further by using actual non-malicious software to hide and pose as typical illegal software versions. ViperSoftX uses these files as ‘carriers’ of the main malware encrypted within the overlay,” Trend Micro noted.
What is even more ominous, Trend Micro observed the primary ViperSoftX C&C servers used for the second stage download changed on a monthly basis.
In the final stage, ViperSoftX main routine will download and install malicious browser extensions, then crawl coin wallets and password managers.
Related Articles
- LockBit 3.0 Ransomware: An evolving threat that challenges network defenses and mitigations
- Royal Ransomware uses a unique “partial encryption approach” to evade detection
- Threat actors abuse Windows debugger tool to disguise PlugX trojan attacks
- Clop: New Linux ransomware variant threat
- Microsoft: RaaS attacks continue to evolve and expand

